How to Upload a File in Html Javascript
Note, this article deals with client-side JavaScript. For a customer and server-side JavaScript upload case, check out this File Uploads with Node and JavaScript tutorial.
It used to be a daunting challenge for a programmer to upload files through a browser. Poor customer-side facilities hampered the equation, and server-side components needed to exist to handle the incoming data stream.
Fortunately, HTML5 file input form tags simplified things on the client side. However, developers take added needless complexity to their awarding when information technology comes to creating Ajax and JavaScript file uploads. When developers plough to popular libraries such as jQuery or Dojo Toolkit, they add unnecessary problems to file uploads. Thankfully, there is an easier way.
| More File Upload Options |
|---|
| I put together a bunch of file upload tutorials. Pick your technology and get uploading!
Uploading files to the server need not be a trouble. |
The easiest and simplest way for a developer to accomplish an Ajax file upload is to utilize pure JavaScript and exit the bulky libraries and frameworks behind.
Ajax file uploads
A developer can perform an Ajax-based file upload to a server with JavaScript in five steps:
- An HTML5 input form chemical element must be included in the webpage that renders in the customer's browser;
- A JavaScript method must be coded to initiate the asynchronous Ajax based file upload;
- A component must be on the server to handle the file upload and save the resource locally;
- The server must send a response to the browser indicating the JavaScript file upload was successful; and
- The customer's browser must provide an Ajax-based response indicating the file uploaded successfully.
In this instance, the JavaScript file upload target is an Apache Web Server. Equally a result, the server-side component that handles the Ajax request will be written in PHP. If a Tomcat or Jetty server was the upload target, a developer could code a Java based uploader on the server-side.
HTML5 file tags
HTML5 introduced a new type of input course field named file. When a browser encounters this tag, it renders a fully functional file picker on the web page. When it'southward combined with an HTML5 button tag that can trigger a JavaScript method, these two elements represent the required markup elements to begin the JavaScript and Ajax file upload process.
The following HTML5 tags provide the required components to add a file selector and an upload push button to any spider web page:
<input id="fileupload" type="file" name="fileupload" /> <button id="upload-button" onclick="uploadFile()"> Upload </button>
The button kicks off a method named uploadFile(), which contains the JavaScript file upload logic.
<script> async part uploadFile() { let formData = new FormData(); formData.suspend("file", fileupload.files[0]); await fetch('/upload.php', { method: "POST", body: formData }); alert('The file has been uploaded successfully.'); } </script>
JavaScript file upload logic
The in a higher place script tag contains null merely pure JavaScript. There's no jQuery or Dojo thrown into the mix and the logic is straightforward:
- Create a FormData object to incorporate the data to be sent to the server;
- Add the chosen file to exist uploaded to the FormData object;
- Asynchronously call server-side resources to handle the upload; and
- The server-side resource is invoked through the Post method
- The server-side resource is passed the FormData which contains the file
- In this example that server-side resource is named upload.php
- When notified that the JavaScript file upload was successful, send an Ajax based alert to the client.
All the HTML and JavaScript logic volition be contained in a unmarried file named uploader.html. The complete HTML looks equally follows:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <title> Ajax JavaScript File Upload Instance </title> </caput> <body> <!-- HTML5 Input Class Elements --> <input id="fileupload" type="file" proper name="fileupload" /> <push id="upload-button" onclick="uploadFile()"> Upload </button> <!-- Ajax JavaScript File Upload Logic --> <script> async part uploadFile() { allow formData = new FormData(); formData.append("file", fileupload.files[0]); look fetch('/upload.php', { method: "POST", trunk: formData }); alert('The file has been uploaded successfully.'); } </script> </body> </html>
Apache file upload processing
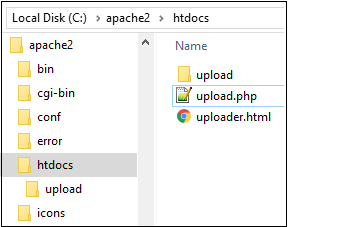
Required JavaScript file upload components.
When an asynchronous JavaScript file upload happens, a server-side component must exist to handle the incoming file and shop it. Since this example uses an Apache HTTP Server (AHS), and since PHP is the language of AHS, it requires a file named upload.php that contains a small PHP script to save the incoming file to a folder named uploads:
<?php /* Become the name of the uploaded file */ $filename = $_FILES['file']['proper noun']; /* Cull where to salvage the uploaded file */ $location = "upload/".$filename; /* Save the uploaded file to the local filesystem */ if ( move_uploaded_file($_FILES['file']['tmp_name'], $location) ) { echo 'Success'; } else { echo 'Failure'; } ?>
The PHP script is also straightforward. Information technology obtains the name of the file beingness uploaded, then creates a spot in a folder named upload to relieve the file. PHP's move_uploaded_file method is then used to salvage the uploaded file to this new location.
Run the JavaScript file upload case
The files used in this example, forth with a folder named upload, must be added to the htdocs binder of AHS. When a client accesses the uploader.html file through a browser, the client volition be able to upload a file to the server using Ajax and pure JavaScript.
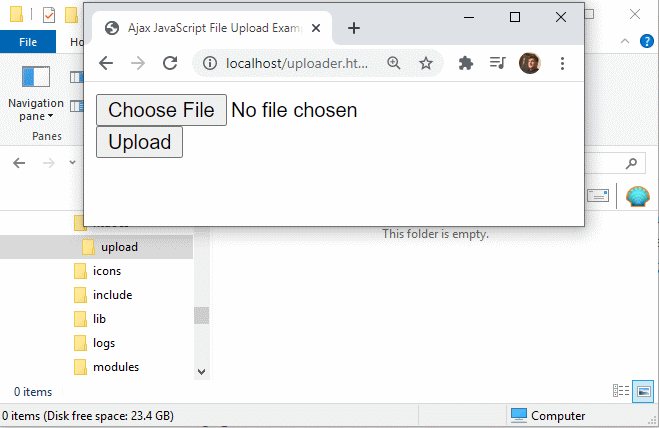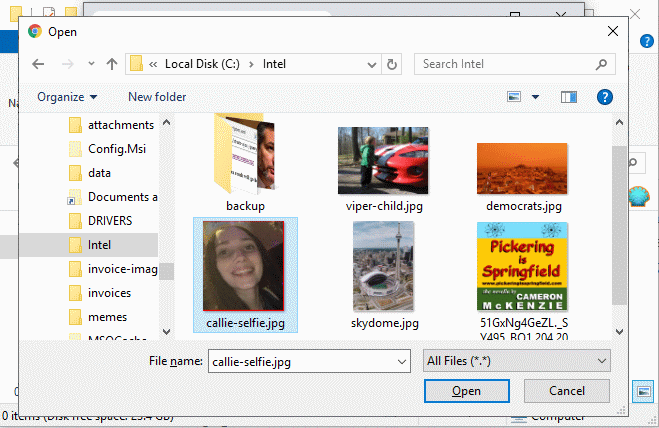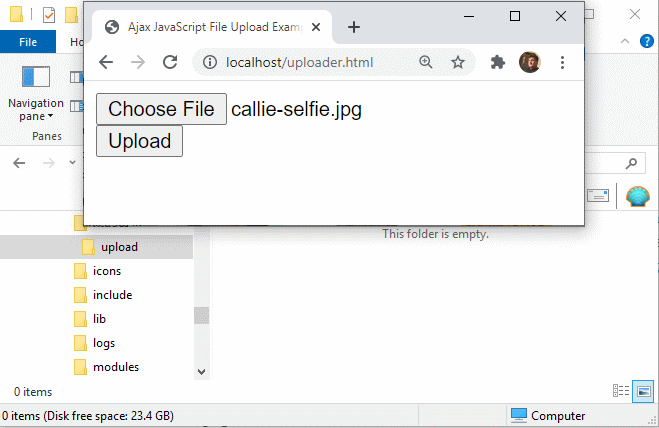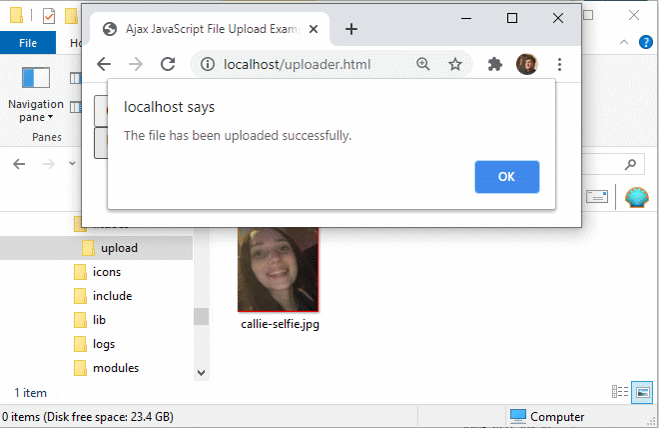
A pure JavaScript file uploader simplifies Ajax based interactions with the server.
Source: https://www.theserverside.com/blog/Coffee-Talk-Java-News-Stories-and-Opinions/Ajax-JavaScript-file-upload-example
0 Response to "How to Upload a File in Html Javascript"
Post a Comment